
First, I will expand a virtual disk of a Linux VM on an ESXi server.
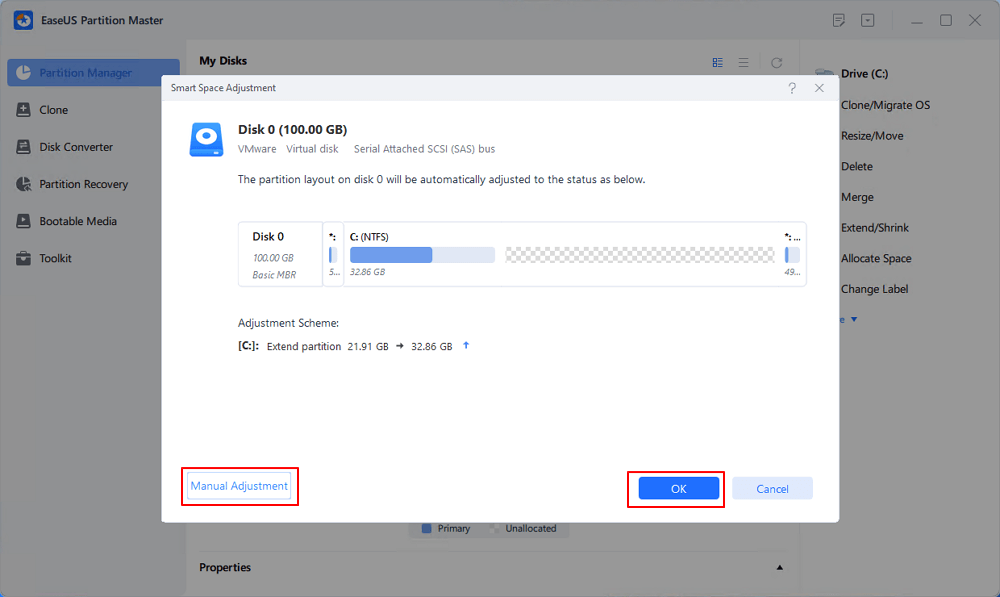
You can use the command line tools or tools with the graphical user interface. There are different methods to adjust disk partition size and extend Linux partitions. In this section, I explain how to extend partitions in Linux after expanding virtual disks. Changing disk partition size may be risky if you make a mistake during the configuration process. It is recommended that you back up your VM before doing operations with disks. If your virtual machine has snapshots, delete them before you resize a virtual disk and adjust disk partition size.
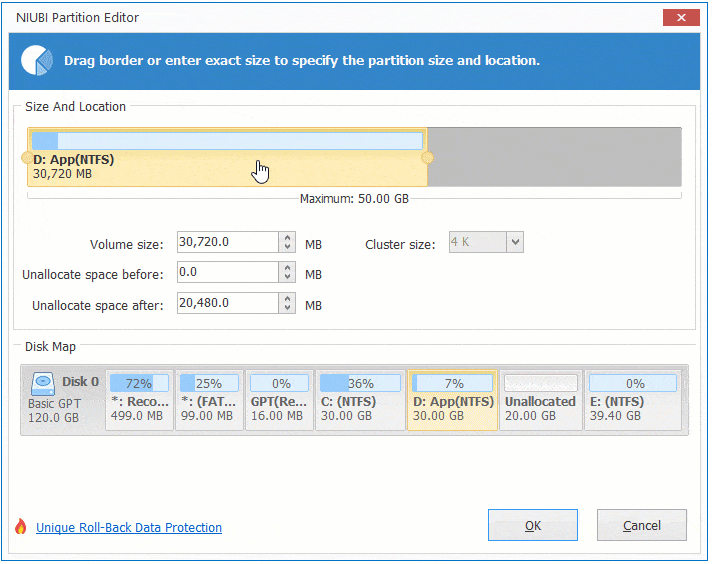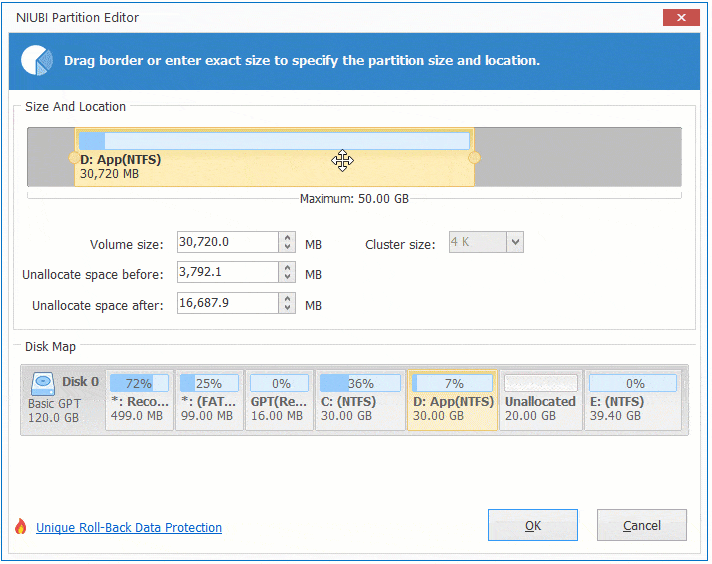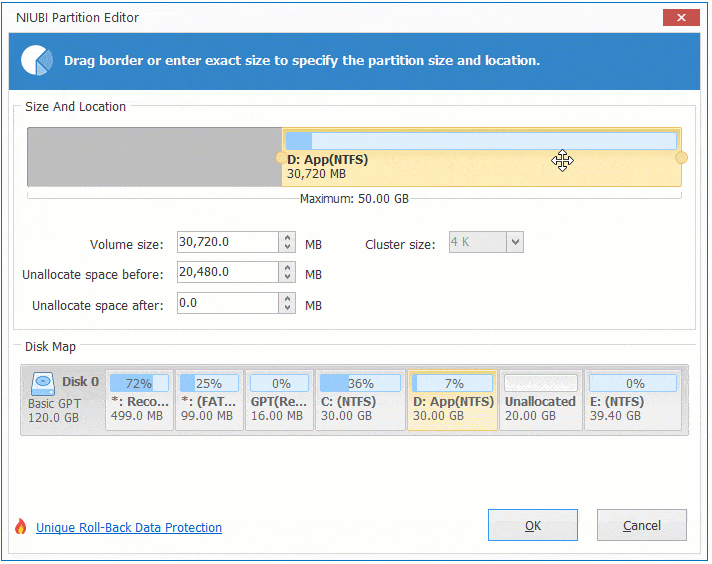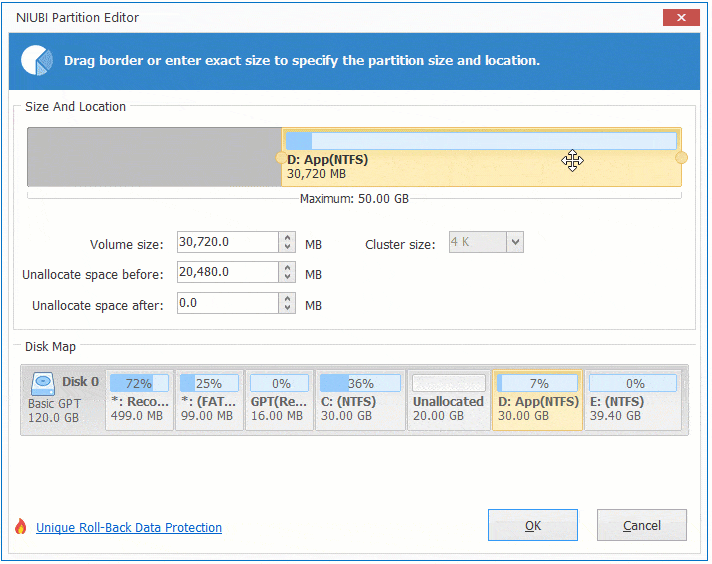
To be resized, a virtual disk must not have snapshots. However, you may need to reboot a VM for the operating system to detect the resized disk. Virtual disk size can be increased while a virtual machine is running. Some conditions must be met before you resize a virtual disk and the partitions on that disk. Using diskpart on the Windows installation medium.Expanding a virtual disk in VMware Workstation.Using diskpart to extend Windows partitions:.Using the Disk Management snap-in in the Windows guest.Expanding a virtual disk in vSphere Client.Extending a partition in the Windows GUI:.Using parted to extend Linux partitions.
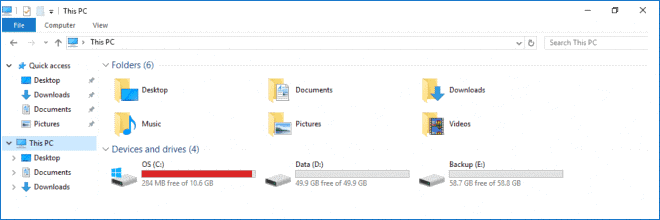
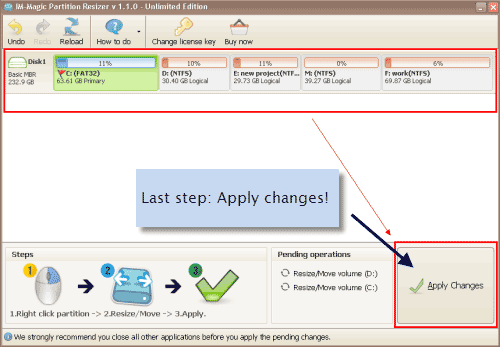
However, you must resize a partition manually after that. With VMware virtualization software providing flexible options to configure virtual hardware such as CPU, memory, and disk devices, you can extend the size of an existing virtual disk. Insufficient disk space on a system partition degrades performance. Later, as you’re working, you realize that performance is suffering because there’s not enough disk space. Let’s imagine this scenario: you’ve created a virtual disk, created partitions, and installed a guest operating system on one of the partitions on that virtual disk. By Michael Bose Increasing the Size of a Disk Partition: A How-to Guide


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
